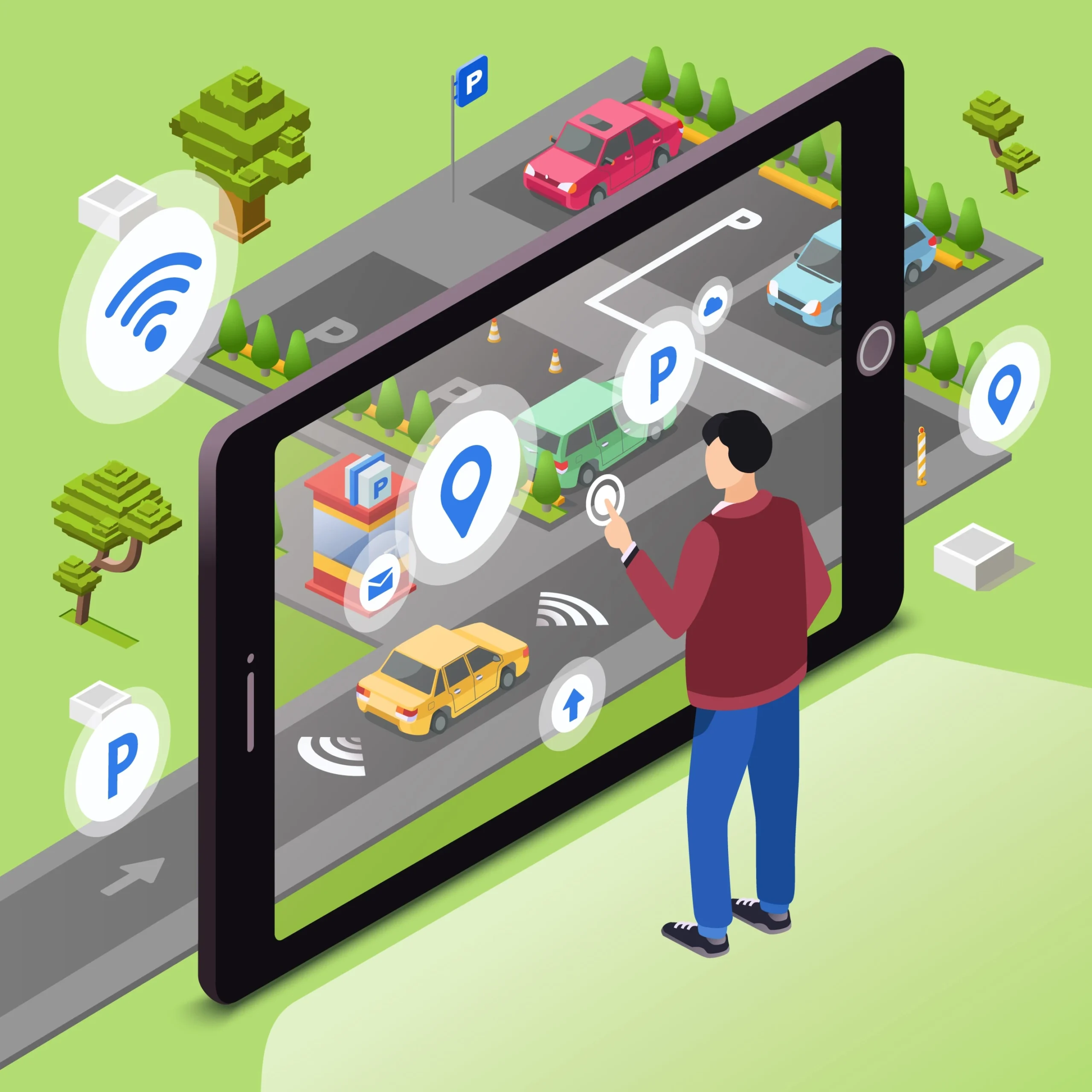
Smart cities are more than just interconnected devices; they are living, breathing ecosystems designed to improve the quality of life for their citizens. And at the heart of any thriving city lies its transportation network. Smart transportation systems are revolutionizing urban mobility, making it safer, more efficient, and more sustainable. This includes not only personal vehicles but also mass transit systems that serve a vital role in urban centers. Why Smart Transportation Matters Reduced Congestion: Traffic jams are a major source of frustration and lost productivity. Smart traffic management systems, powered by real-time data from IoT sensors and cameras, can dynamically adjust traffic flow, optimize routes, and reduce congestion. Enhanced Safety: Smart transportation incorporates advanced safety features such as connected vehicle technology, which allows vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure to prevent accidents. Predictive maintenance systems can also identify potential safety hazards before they lead to breakdowns or accidents. Improved Sustainability: Electric vehicles, optimized routing, and reduced idling contribute to lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. Smart transportation systems can also promote the use of public transportation and shared mobility options, further reducing reliance on personal vehicles. Increased Efficiency: Real-time information on traffic conditions, public transportation schedules, and parking availability empowers citizens to make informed decisions about their travel plans, saving time and reducing stress. Bus Stop Queue [Freepik www.freepik.com] Key Components of Smart Transportation IoT Sensors: These devices collect data on traffic flow, parking occupancy, air quality, and other key metrics, providing a comprehensive picture of the urban environment. Smart Traffic Management Systems: These systems use data analytics and algorithms to optimize traffic signal timing, manage incidents, and provide real-time traffic information to drivers. Connected Vehicles: Vehicles equipped with sensors and communication technology can exchange information with each other and with infrastructure, enabling features such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking. Electric Vehicle Infrastructure: A network of charging stations is essential to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Smart charging systems can optimize charging schedules to minimize grid impact and reduce energy costs. E-Governance Platforms: Citizens can use mobile apps and online portals to access transportation information, pay for parking, report issues, and provide feedback to city officials. Mass Transit Integration Mass transit is a critical component of smart transportation, offering high-capacity, efficient, and sustainable mobility options within urban areas. Integrating mass transit into a smart city framework involves several key strategies: Real-Time Information Systems: Providing passengers with real-time information on bus and train arrival and departure times, potential delays, and service disruptions enhances the overall transit experience. Digital displays at bus stops and mobile apps can deliver this information directly to riders. Integrated Payment Systems: Smart fare payment systems, such as mobile ticketing and contactless payment options, streamline the boarding process and improve efficiency. Optimized Routing and Scheduling: Data analytics and AI algorithms can be used to optimize bus and train routes and schedules based on passenger demand and traffic conditions. This ensures that transit services are aligned with the needs of the community and are operating at peak efficiency. Enhancing Public Safety at Mass Transit Stops Ensuring the safety and security of passengers at mass transit stops is paramount. Several smart city technologies can be deployed to enhance public safety: Smart Lighting: Adequate lighting is essential for creating a safe and secure environment at bus stops and transit stations. Smart LED lights can be equipped with sensors that automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light levels and pedestrian activity, improving visibility and deterring crime. Surveillance Systems: Security cameras can be strategically placed at transit stops to monitor activity and deter criminal behavior. Real-time video feeds can be monitored by transit authorities and law enforcement, allowing for rapid response to incidents. Emergency Communication Systems: Installing emergency call boxes or buttons at transit stops provides passengers with a direct line to transit authorities or emergency services. These systems can be particularly valuable in isolated or high-crime areas. Protective Barriers: Metro in Los Angeles has finalized the installation of protective barriers on its entire bus fleet to protect drivers from physical attacks. These barriers, made of shatterproof, tempered glass, have been shown to reduce assaults on bus operators by 58%. Examples in Action GoTriangle (North Carolina): GoTriangle uses a Rider App to allow passengers to track buses in real time and provides service alerts via its website and social media channels. The agency also has an adverse weather plan to maintain the well-being of riders and employees during inclement weather. Los Angeles Metro: Metro has equipped its entire bus fleet with protective barriers for drivers to reduce assaults. The agency has also added onboard cameras, digital video recorders, and emergency buttons that operators can use to call for help. Miami-Dade Transit: Miami-Dade Transit integrates various smart technologies to improve public transport. SELS: Smart Era Lighting has been designing and building smart, solar powered LED lights and bus stops. Agencies around the US are using these to provide an illuminated location for passengers. The Road Ahead Smart transportation is not just about technology; it’s about creating a more livable, sustainable, and equitable future for our cities. By embracing innovation and working together, we can transform our transportation networks, including mass transit systems, into engines of economic growth and social progress. The Smart Transport Symposium, and similar events, are crucial for fostering these discussions and driving innovation forward. Smart Mobility Symposium Varidx is organizing a Smart Transport symposium on April 17 with transportation leaders from the Triangle. In Partnership with: 📅 Date: April 17, 2025 ⏰ Time: 3-5 PM 📍 Location: Central Pines Regional Council, 4307 Emperor Blvd, Suites 110, Durham, NC 2770 Register Now!
Smart cities are more than just interconnected devices; they are living, breathing ecosystems designed to improve the quality of life for their citizens. And at the heart of any thriving city lies its transportation network. Smart transportation systems are revolutionizing urban mobility, making it safer, more efficient, and more sustainable. This includes not only personal vehicles but also mass transit systems that serve a vital role in urban centers.
Why Smart Transportation Matters
- Reduced Congestion: Traffic jams are a major source of frustration and lost productivity. Smart traffic management systems, powered by real-time data from IoT sensors and cameras, can dynamically adjust traffic flow, optimize routes, and reduce congestion.
- Enhanced Safety: Smart transportation incorporates advanced safety features such as connected vehicle technology, which allows vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure to prevent accidents. Predictive maintenance systems can also identify potential safety hazards before they lead to breakdowns or accidents.
- Improved Sustainability: Electric vehicles, optimized routing, and reduced idling contribute to lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. Smart transportation systems can also promote the use of public transportation and shared mobility options, further reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
- Increased Efficiency: Real-time information on traffic conditions, public transportation schedules, and parking availability empowers citizens to make informed decisions about their travel plans, saving time and reducing stress.
Bus Stop Queue [Freepik www.freepik.com]
Key Components of Smart Transportation
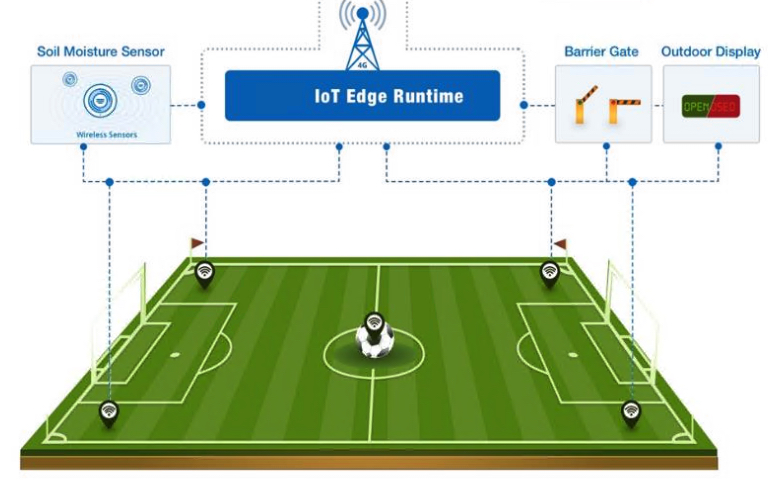
- IoT Sensors: These devices collect data on traffic flow, parking occupancy, air quality, and other key metrics, providing a comprehensive picture of the urban environment.
- Smart Traffic Management Systems: These systems use data analytics and algorithms to optimize traffic signal timing, manage incidents, and provide real-time traffic information to drivers.
- Connected Vehicles: Vehicles equipped with sensors and communication technology can exchange information with each other and with infrastructure, enabling features such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking.
- Electric Vehicle Infrastructure: A network of charging stations is essential to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Smart charging systems can optimize charging schedules to minimize grid impact and reduce energy costs.
- E-Governance Platforms: Citizens can use mobile apps and online portals to access transportation information, pay for parking, report issues, and provide feedback to city officials.
Mass Transit Integration
Mass transit is a critical component of smart transportation, offering high-capacity, efficient, and sustainable mobility options within urban areas. Integrating mass transit into a smart city framework involves several key strategies:
- Real-Time Information Systems: Providing passengers with real-time information on bus and train arrival and departure times, potential delays, and service disruptions enhances the overall transit experience. Digital displays at bus stops and mobile apps can deliver this information directly to riders.
- Integrated Payment Systems: Smart fare payment systems, such as mobile ticketing and contactless payment options, streamline the boarding process and improve efficiency.
- Optimized Routing and Scheduling: Data analytics and AI algorithms can be used to optimize bus and train routes and schedules based on passenger demand and traffic conditions. This ensures that transit services are aligned with the needs of the community and are operating at peak efficiency.
Enhancing Public Safety at Mass Transit Stops
Ensuring the safety and security of passengers at mass transit stops is paramount. Several smart city technologies can be deployed to enhance public safety:
- Smart Lighting: Adequate lighting is essential for creating a safe and secure environment at bus stops and transit stations. Smart LED lights can be equipped with sensors that automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light levels and pedestrian activity, improving visibility and deterring crime.
- Surveillance Systems: Security cameras can be strategically placed at transit stops to monitor activity and deter criminal behavior. Real-time video feeds can be monitored by transit authorities and law enforcement, allowing for rapid response to incidents.
- Emergency Communication Systems: Installing emergency call boxes or buttons at transit stops provides passengers with a direct line to transit authorities or emergency services. These systems can be particularly valuable in isolated or high-crime areas.
- Protective Barriers: Metro in Los Angeles has finalized the installation of protective barriers on its entire bus fleet to protect drivers from physical attacks. These barriers, made of shatterproof, tempered glass, have been shown to reduce assaults on bus operators by 58%.
Examples in Action
- GoTriangle (North Carolina): GoTriangle uses a Rider App to allow passengers to track buses in real time and provides service alerts via its website and social media channels. The agency also has an adverse weather plan to maintain the well-being of riders and employees during inclement weather.
- Los Angeles Metro: Metro has equipped its entire bus fleet with protective barriers for drivers to reduce assaults. The agency has also added onboard cameras, digital video recorders, and emergency buttons that operators can use to call for help.
- Miami-Dade Transit: Miami-Dade Transit integrates various smart technologies to improve public transport.
- SELS: Smart Era Lighting has been designing and building smart, solar powered LED lights and bus stops. Agencies around the US are using these to provide an illuminated location for passengers.

The Road Ahead
Smart transportation is not just about technology; it’s about creating a more livable, sustainable, and equitable future for our cities. By embracing innovation and working together, we can transform our transportation networks, including mass transit systems, into engines of economic growth and social progress. The Smart Transport Symposium, and similar events, are crucial for fostering these discussions and driving innovation forward.
Smart Mobility Symposium
📅 Date: April 17, 2025
⏰ Time: 3-5 PM
📍 Location: Central Pines Regional Council, 4307 Emperor Blvd, Suites 110, Durham, NC 2770
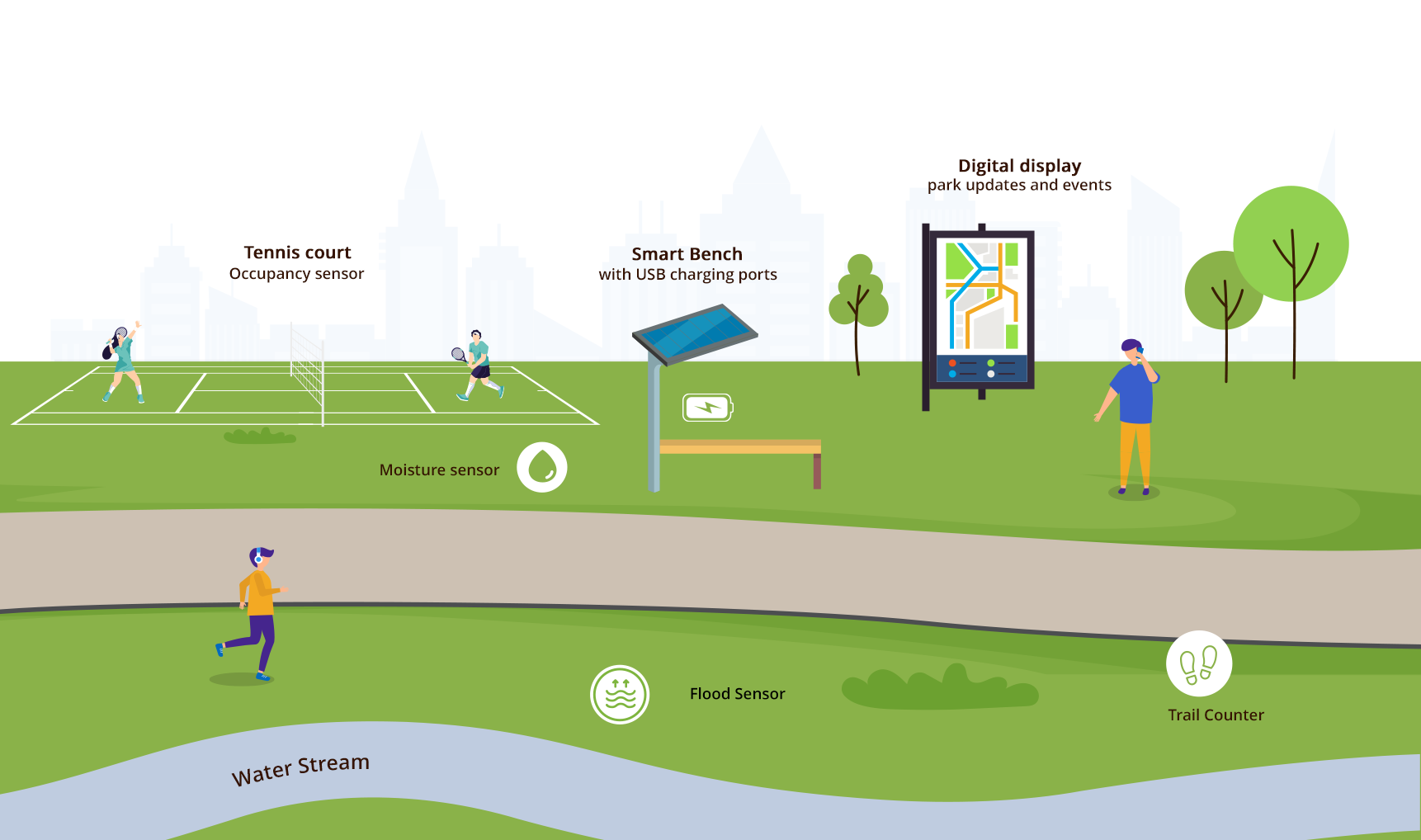
As urban landscapes evolve, so do the green spaces within them. Today’s parks are no longer just passive recreational areas; they’re becoming dynamic, responsive environments that leverage cutting-edge technology to enhance visitor experiences and contribute to broader smart city initiatives. Let’s explore three exciting trends that are reshaping our urban oases. 1. Smart Benches: More Than Just a Place to Sit Gone are the days when park benches were simply places to rest. The new generation of smart benches is transforming these humble fixtures into multifunctional hubs of connectivity and convenience. Solar-Powered Connectivity Smart benches often come equipped with solar panels, allowing them to generate their own clean energy. This self-sufficiency not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with cities’ sustainability goals. Charging Stations on the Go One of the most appreciated features of smart benches is their ability to charge mobile devices. USB ports and wireless charging pads are seamlessly integrated into the design, allowing park-goers to top up their batteries while enjoying the outdoors. Wi-Fi Hotspots Many smart benches double as Wi-Fi hotspots, extending internet connectivity throughout the park. This feature not only enhances visitor convenience but also supports various IoT devices and sensors deployed in the area. Environmental Monitoring Some advanced models incorporate sensors that monitor air quality, temperature, and humidity. This data can be invaluable for city planners and environmental scientists tracking urban microclimates and pollution levels. Interactive Information Displays Touchscreen displays on smart benches can provide park maps, event schedules, and real-time information about park facilities. Some even offer interactive games or educational content about local flora and fauna. The integration of smart benches is just the beginning. As these technologies become more widespread, we can expect to see increased engagement from park visitors and more efficient management of park resources. 2. Intelligent Irrigation: Precision Water Management Water conservation is a critical concern for many cities, and parks are often significant consumers of this precious resource. Intelligent irrigation systems are emerging as a game-changer in park management, offering precision control and substantial water savings. Soil Moisture Sensors By embedding sensors throughout park grounds, irrigation systems can now detect the exact moisture content of the soil. This granular data allows for targeted watering, ensuring that each area receives precisely the amount of water it needs – no more, no less. Weather-Based Controls Advanced irrigation systems integrate local weather forecasts into their decision-making processes. If rain is predicted, the system can automatically adjust or postpone watering schedules, preventing wasteful overwatering. Leak Detection Intelligent systems can quickly identify unusual water flow patterns that may indicate leaks. This rapid response capability can save thousands of gallons of water and prevent damage to park infrastructure. Remote Management Park managers can now control irrigation systems from their smartphones or tablets. This remote access allows for real-time adjustments and rapid response to changing conditions, even when staff are not physically present in the park. Data-Driven Landscaping The wealth of data collected by these systems is helping park designers make more informed decisions about plant selection and placement. By understanding microclimates within the park, they can choose species that will thrive in specific locations, reducing the need for intensive irrigation. The implementation of intelligent irrigation not only conserves water but also promotes healthier plant growth, reduces maintenance costs, and allows parks to remain lush and inviting even in drought-prone areas. 3. Climate Resilience: Parks as Urban Safeguards As cities grapple with the impacts of climate change, parks are being reimagined as critical infrastructure for climate resilience. Innovative technologies are enabling these green spaces to play a vital role in mitigating environmental challenges. Flood Mitigation Through Smart Design Parks in flood-prone areas are being redesigned with permeable surfaces and underground water storage systems. Smart sensors monitor water levels and can automatically activate pumps or open drainage channels to manage excess water during heavy rainfall events. Urban Heat Island Reduction Strategic placement of trees and green spaces, guided by thermal imaging and microclimate sensors, helps combat the urban heat island effect. Some parks are experimenting with “cool pavements” that reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat than traditional materials. Air Quality Improvement Beyond passive air filtration by vegetation, some parks are installing active air purification systems. These can range from photocatalytic surfaces that break down pollutants to strategically placed “smog-eating” sculptures that filter particulates from the air. Biodiversity Monitoring Advanced camera systems and AI-powered image recognition are being used to track wildlife populations and plant health. This data helps park managers maintain ecological balance and respond quickly to invasive species or disease outbreaks. Renewable Energy Generation Some forward-thinking parks are incorporating renewable energy generation into their design. Solar walkways, wind turbines disguised as public art, and even piezoelectric systems that generate electricity from footsteps are turning parks into clean energy producers. Community Education and Engagement Interactive displays and augmented reality apps are being used to educate visitors about climate change and resilience strategies. Some parks host “living labs” where visitors can see climate adaptation techniques in action and learn how to apply them in their own lives. By embracing these climate resilience technologies, parks are not only protecting themselves from environmental threats but are also serving as models for sustainable urban development. The Future is Green and Smart As we’ve seen, the integration of technology into urban parks is creating spaces that are more engaging, efficient, and resilient. Smart benches are redefining how we interact with park amenities, intelligent irrigation is revolutionizing water management, and climate resilience strategies are positioning parks as crucial components of sustainable urban infrastructure. These advancements are not just about adding gadgets to our green spaces. They represent a fundamental shift in how we conceive of parks in the urban fabric. Parks are becoming active participants in city life, contributing to data collection, environmental management, and community engagement in ways that were unimaginable just a few years ago. As we look to the future, we can expect to see even greater integration between parks and
Parks and Recreation directors across the country are embracing innovative technologies to enhance their operations and visitor experiences. Here’s how cutting-edge tech is reshaping the landscape of community green spaces and recreational programs: 1. Smart Park Wi-Fi: The Digital Oasis Many directors have found that implementing Wi-Fi throughout their parks is a game-changer. Visitors are staying longer, sharing their experiences on social media, and inadvertently becoming brand ambassadors for these green spaces. It’s a win-win situation that boosts engagement and provides free marketing for parks. 2. Virtual Tours and Augmented Reality: Parks Without Borders Virtual tours have become an essential tool for Parks and Rec departments. These digital experiences allow people to explore parks from the comfort of their homes, making them accessible to those with mobility challenges or those planning future visits. But the excitement doesn’t stop there! Augmented Reality (AR) and Extended Reality (XR) are taking park visits to a whole new level. Imagine visitors pointing their smartphones at a tree and instantly seeing information about its species, age, and ecological importance. Or picture families going on AR-powered scavenger hunts that blend the digital and natural worlds. These technologies are not just enhancing visits; they’re creating entirely new ways to interact with and learn from our parks. 3. Streamlined Online Registration: Say Goodbye to Paperwork Online registration systems have revolutionized how departments manage program sign-ups. Directors report significant increases in participation for summer camps, fitness classes, and other activities. The ease of use for both staff and community members has made this technology a must-have for modern Parks and Rec departments. 4. Mobile Apps: Parks in Your Pocket Department-specific mobile apps have become indispensable tools for both visitors and staff. These apps provide easy access to trail maps, event schedules, and real-time updates about park conditions. But the functionality doesn’t stop there. Many directors are now incorporating features that provide real-time occupancy status for popular amenities like pickleball and tennis courts. Imagine a park visitor checking their phone to see if a court is available before making the trip. Some apps even integrate with weather warning systems, sending push notifications when a soccer field needs to be closed due to lightning strikes in the area. This level of real-time information not only enhances the visitor experience but also improves safety and resource management. 5. IoT Sensors: The Silent Park Managers Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are proving to be invaluable assets for park management. These small but mighty devices collect data on everything from soil moisture levels to playground equipment usage. Directors are using this information to make data-driven decisions that improve park maintenance and visitor experiences. 6. Operational Efficiency Technologies: Working Smarter, Not Harder Parks and Rec directors are implementing a variety of technologies to boost operational efficiency: Smart irrigation systems are reducing water waste by up to 25% in some parks. Automated maintenance scheduling software is helping teams allocate resources more effectively. Waste management sensors in trash bins are optimizing collection routes. Digital asset management software is reducing maintenance response times by as much as 40%. Drone technology is making inspections of hard-to-reach areas safer and more efficient. These innovations are not only improving park operations but also freeing up resources for other community-focused initiatives. 7. Energy Harvesting Systems: Parks That Power Themselves Forward-thinking directors are exploring energy harvesting technologies to make their parks more sustainable. Solar-powered benches that charge visitors’ devices and kinetic energy tiles on busy walkways are just the beginning. These innovations are helping parks generate their own electricity, reducing energy costs and environmental impact. As Parks and Recreation directors look to the future, the potential for technology to enhance community green spaces seems limitless. From AR-powered nature walks to AI-driven program recommendations, the parks of tomorrow promise to be more engaging, accessible, and sustainable than ever before. By embracing these technological advancements, directors aren’t just improving their parks – they’re reimagining what a park can be in the 21st century. It’s an exciting time to be in Parks and Recreation, and the innovations on the horizon promise to keep our green spaces at the forefront of community life for generations to come.
In our previous posts, we explored the foundational concepts of smart cities and detailed the essential technologies needed for implementation. Now, let’s dive into how cities can practically kickstart their smart city initiatives, drawing insights from a recent webinar presented by Varidx, an award-winning smart city solutions provider. The Smart City Evolution: From Concept to Reality The journey to becoming a smart city isn’t just about implementing technology – it’s about creating meaningful impact for residents. As we’ve seen in our earlier discussions, successful smart cities focus on efficiently using digital technologies to improve service delivery, operational efficiency, and quality of life for residents. Key Steps for Implementation 1. Start with Assessment and Planning Before diving into technology deployment, cities must thoroughly evaluate their existing infrastructure and capabilities. This includes: Network connectivity coverage Existing sensor deployments Data management systems Technical expertise within departments Current digital services 2. Identify Clear Priorities and Problems The most successful smart city initiatives begin by addressing specific community challenges. For example, the Town of Morrisville started with practical problems in their parks department: Checking wet soccer fields manually was time-consuming Inefficient trash collection schedules Limited data on trail utilization Need for better field closure communication 3. Choose the Right Pilot Project When selecting an initial project, consider these three key criteria: Quick Implementation (3-6 months) Budget-Friendly (Under $50K investment) Direct Citizen Impact Some recommended pilot options include: Smart Parks (moisture sensors, occupancy monitoring) Air Quality Monitoring Smart Street Lighting 4. Secure Stakeholder Buy-in As highlighted in our previous post about implementation strategies, stakeholder engagement is crucial. The webinar emphasized creating a comprehensive engagement framework including: Core city leadership – This group drives strategic direction and ensures alignment with city priorities. Key players include city manager, CIO, and department heads. Emphasize: Governance and decision-making authority. Citizens and community groups – Residents are both beneficiaries and active participants. Engage through digital platforms and town halls. Local businesses – Local businesses bring expertise and investment opportunities. They help identify economic development priorities. Such as downtown smart parking initiative. Technology partners – Provide technical expertise and implementation support. Help evaluate solution feasibility. Bring experience from other cities. Instead of just buying technology, build long-term partnerships Infrastructure providers – Essential for system integration, who manage critical city services 5. Measure and Communicate Benefits Successful smart city initiatives track and communicate clear benefits across three key areas: Financial Benefits: 20-30% reduction in operational costs ROI within 24-36 months 10-15% improvement in satisfaction Community Impact: 20-50% improved community engagement 24/7 digital service access Enhanced citizen experience Environmental Impact: 10-25% reduction in energy consumption 10-20% decrease in carbon emissions 10-25% less water waste Real-World Success Stories The webinar shared several inspiring case studies, including Morrisville’s award-winning Connected Parks initiative. Starting with a focused pilot project using trail counters, they expanded to include flood sensors and other smart technologies, demonstrating how cities can grow their smart initiatives incrementally. Avoiding Common Pitfalls The presentation highlighted several key considerations to ensure success: Avoid the “technology first” trap – start with citizen needs. Example: Cities buying IoT platforms without clear use cases. Better approach: Start with specific problems to solve. Don’t fall for the “build it, they’ll come” myth . Without community engagement, the result will be Low adoption rates and wasted resources. For better results, engage stakeholders from day one. Skip the “big bang” approach. Trying to do everything at once, creates overwhelming complexity. Instead: Start small, prove value, then expand. Looking Ahead As we move through 2025, cities have more opportunities than ever to leverage smart technologies effectively. The key is to start with clear objectives, choose focused pilot projects, and build on successes while maintaining strong stakeholder engagement. Remember that becoming a smart city is a journey, not a destination. By following these structured steps and learning from successful implementations, cities of any size can begin their transformation into more efficient, sustainable, and livable communities. Ready to start your smart city journey? Our next post will dive deeper into specific technologies and solutions that can help you achieve your smart city goals. Stay tuned! Want to learn more about smart city implementation? Check out our previous posts on Smart City Technologies and Solutions and Building a Smart City Foundation. Ready to be part of the urban revolution? Varidx can help your city with the smart city assessment and find the right technologies to start smart city implementation that meet local requirements! Book an appointment to discuss your needs.
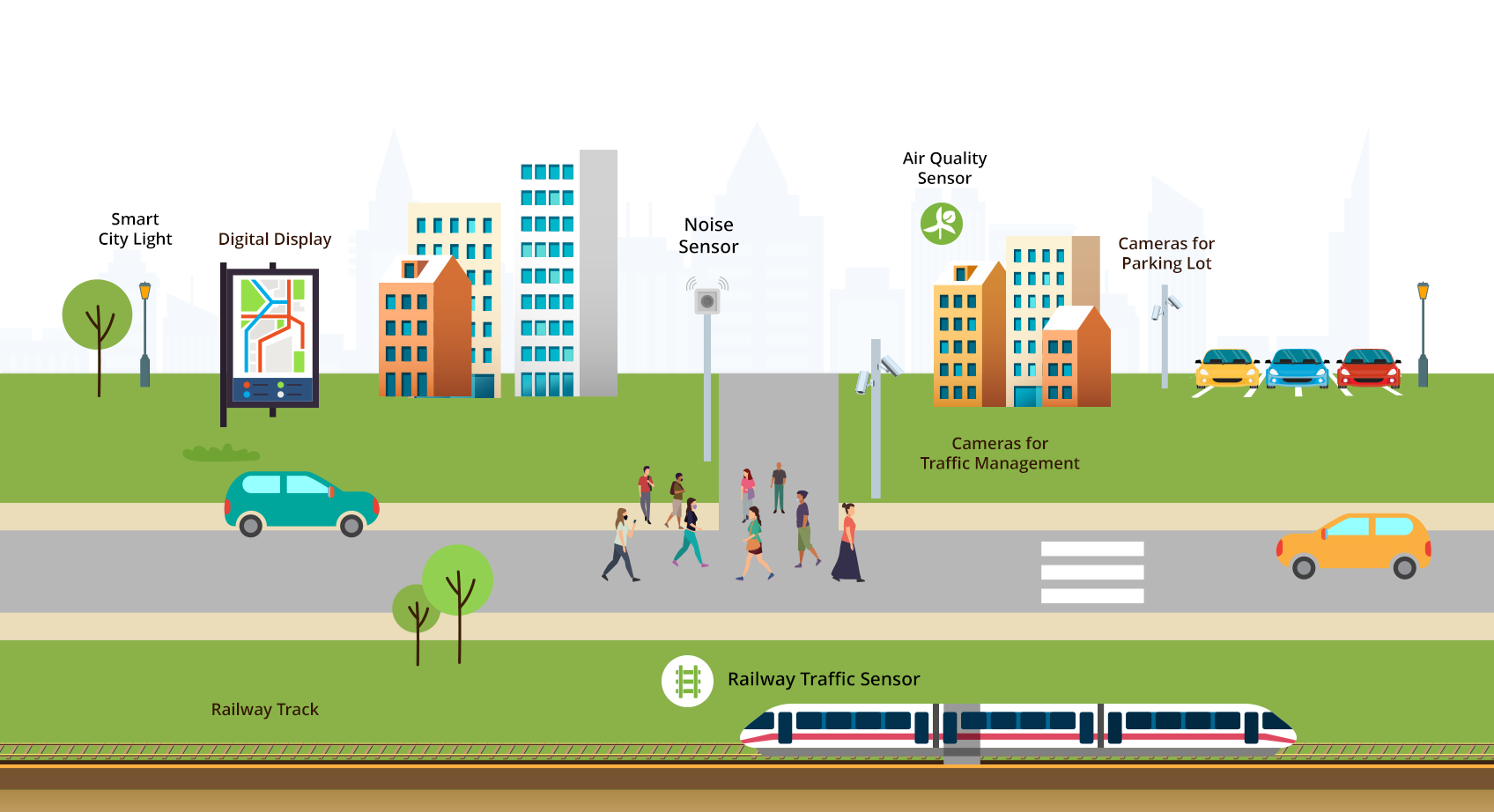
In our previous post, we introduced the concept of smart cities and their transformative potential. Now, let’s dive deeper into how cities can systematically implement smart technologies to achieve their goals. This practical guide will walk through the essential steps and technologies needed to begin your smart city journey. Step 1: Assess Your Current Infrastructure Before implementing any new technology, cities must thoroughly evaluate their existing infrastructure and capabilities. According to a McKinsey Global Institute report (2018), cities that conduct comprehensive baseline assessments are 2.5 times more likely to succeed in their smart city initiatives. Key Assessment Areas: Network connectivity coverage and capacity Existing sensor deployments and IoT infrastructure Data management systems and integration capabilities Technical expertise within city departments Current digital services and citizen engagement platforms Real-World Example: Barcelona’s digital transformation began with a comprehensive audit of its technology infrastructure in 2011. This assessment helped identify gaps and prioritize investments, leading to the successful implementation of over 200 smart city initiatives (Angelidou, 2017). Step 2: Establish Your Technology Foundation Based on your assessment, build the fundamental infrastructure required to support smart city applications. Research by Deloitte (2019) indicates that 40% of smart city project failures stem from inadequate underlying infrastructure. Essential Components: 1. Connectivity Infrastructure: High-speed fiber optic networks 5G wireless coverage (or NB-IOT for low bandwidth sensors) Low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN or LoRaWAN) for IoT devices Public WiFi networks 2. IoT Sensor Network: Environmental sensors (air quality, noise, temperature, soil moisture) Flood monitors on streams to measure water level Occupancy sensors to identify whether a facility (room, pickleball court, tennis court etc.) is occupied Trail counter to track number of people using a particular trail Traffic and mobility sensors to count cars, bicycles on a street Utility monitors tracking usage of water, electricity or gas Infrastructure health sensors monitoring status of HVAC units, buildings or bridges 3. Actuation Devices: Barrier gates to open/close access to areas Access control for facilities Digital displays to update city events, activities, facility open/close notification. Lighting control for fields and facilities Control valves for plumbing 4. Camera Network: Surveillance cameras for security Traffic cameras integrated in Intelligent Traffic Management systems License Plate Reader (LPR) in a parking lot or street for surveillance Mobile or portable camera devices for temporary monitoring Case Study: Singapore’s Smart Nation Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative began by deploying a comprehensive network of 110,000 lampposts equipped with sensors, creating a foundational IoT infrastructure for multiple applications (Smart Nation Singapore, 2021). Step 3: Implement Data Management Systems A robust data management framework is crucial for handling the vast amounts of data generated by smart city systems. IDC predicted that by this year (2025), smart cities will generate over 181 zettabytes of data annually (IDC, 2021). I don’t know if we are on track, but the cities are generating a lot of data from the various monitoring tools. Surveillance cameras are possibly generating several terabytes of data. Key Components: 1. Data Platform: Central data repository Data integration capabilities Analytics tools Visualization dashboards 2. Security Measures: End-to-end encryption Access control systems Privacy protection mechanisms Regular security audits Example Implementation: Helsinki’s 3D Digital Twin platform integrates data from multiple sources and provides visualization tools for urban planning and citizen engagement (Forum Virium Helsinki, 2021). Step 4: Deploy Pilot Projects Every city is unique from Smart City implementation perspective, it’s leaders and residents are going to have different priorities. Larger cities may emphasize intelligent traffic management systems with air quality monitors for internal roads, while cities close to interstate highways want air quality and noise monitoring to understand the impact of passing traffic on it’s neighborhoods. Both cases solve problems for a community, but the approach to implementation is going to vary. Focus on a small subset of the problem and try the technology end-to-end. Deploy sensors in the field to collect data Deploy a dashboard for city staff to view and analyze this data to make decisions Share dashboard with residents to show relevant information Create reports from the dashboard to share with senior management and elected officials Build partnerships with vendors who can help recommend technologies and integrate different parts to build a complete solution Communicate. Use digital media, social media, events, meetings to discuss the plans and solutions The pilot project should result in a clear plan for the next steps and answer the following questions Are the priorities of all the stakeholders aligned for the future implementations? Did the solution provide relevant and timely answers? What part of technology needs to be tweaked or enhanced? Has the right partner been identified to execute these steps? What are the phases for future implementation? From the early wins, build support for future projects. During this stage it is important to identify the right people and the implementation phases. Step 5: Deploy Smart Applications With the foundation in place, begin implementing specific smart city applications based on your city’s priorities. Research by the ESI ThoughtLab (2021) shows that cities see an average ROI of 3-4% on smart city investments. Popular Starting Points: 1. Smart Lighting Energy savings: 50-70% reduction in electricity consumption Enhanced public safety Improved maintenance efficiency 2. Intelligent Transportation Traffic optimization Public transit improvements Parking management 3. Environmental Monitoring Air quality tracking Noise level monitoring Weather data collection Success Story: Copenhagen’s intelligent traffic management system reduced average travel times by 17% and carbon emissions by 8% (Copenhagen Solutions Lab, 2020). Step 6: Enable Citizen Engagement According to Gartner (2021), citizen engagement is crucial for smart city success, with projects involving active citizen participation showing 30% higher success rates. Essential Elements: 1. Digital Services Platform: Mobile applications Online portals Service request systems Real-time information dashboards 2. Feedback Mechanisms: Citizen reporting tools Community forums Social media integration Satisfaction surveys Case Study: Seoul’s Smart City Platform Seoul’s Smart City platform allows citizens to propose and vote on city initiatives, leading to over 5,800 implemented suggestions since 2017 (Seoul Metropolitan Government, 2021). Step 7: Monitor and Optimize Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential
What is a Smart City? What exactly is a “smart city”? While tech companies often focus on flashy sensors and apps, a truly smart city is one that thoughtfully integrates technology, community engagement, and environmental considerations to enhance quality of life, sustainability, and resilience for all residents. Rather than starting with technology for technology’s sake, successful smart city initiatives begin by identifying real community challenges that need solving. For example, the City of Richmond, California faced serious air quality issues affecting public health due to industrial activity, ports, and highways near residential areas. They launched a targeted project to gather data on pollution sources and develop evidence-based improvement plans. They deployed 50 air quality sensors and enrolled citizens to collect additional data as a part of California Air Resources Board (CARB). Step 1: Measurable Outcomes When launching a smart city program, focus first on defining clear, measurable outcomes tied to community priorities. These could include: Reducing traffic congestion and commute times by 25% through smart traffic signals and real-time transit information Cutting energy usage and costs by 30% via smart building systems and LED streetlights Improving emergency response times by 40% through connected infrastructure and predictive analytics Increasing civic engagement by enabling 24/7 access to city services and public input channels Step 2: Stakeholder Engagement Most importantly, successful initiatives require buy-in and ongoing engagement from key stakeholders: City leadership to champion the vision and secure resources Department heads to enable cross-agency collaboration Community members to ensure solutions meet real needs Local businesses and institutions as potential partners Technology vendors aligned with city goals The Town of Morrisville provides a model approach. Town of Morrisville started with a strategic plan organized around core community values: sustainability, mobility, accessibility, resiliency and transparency. The town created a Smart City Advisory Committee that meets on a regular basis. The committee reviews the proposals and makes recommendations about technology and implementation. Resident surveys about their technology needs and concerns are conducted. Based on this input, they evaluate and implement specific technologies. The key is viewing smart city development as a means to an end – using technology thoughtfully to create measurable improvements in residents’ daily lives. By starting with community challenges rather than technology solutions, cities can develop initiatives that deliver real value. Want to get started? Begin by: Step 3: Leveraging Existing Resources A common misconception is that smart city initiatives require massive new investments. In reality, many communities already have valuable infrastructure and data sources they can leverage: Existing Infrastructure USGS flood monitoring stations providing real-time water level data Building automation systems in government facilities HVAC systems generating performance data through industry-standard protocols (BACnet, Modbus, DNP3) Traffic signals and cameras Weather stations Local Technology Partners IT service providers System integrators Software development firms Telecommunications companies Cybersecurity specialists Academic Partners Many universities are eager to collaborate on smart city projects through their specialized departments: Forestry departments for urban tree monitoring and park management Environmental engineering for air quality assessment Civil engineering for flood monitoring and infrastructure analysis Computer science for data analytics and visualization Urban planning for community engagement and impact assessment Data as Currency The data generated through smart city initiatives has real value that can help fund future projects: Share data with private partners in exchange for services Generate insights that improve operational efficiency Support grant applications with evidence-based outcomes Create new revenue streams through data monetization Demonstrate ROI to secure additional funding For example, Philadelphia uses a “Pitch & Pilot” framework where companies can propose solutions to city challenges. Successful pilots can lead to broader implementation, with companies gaining valuable real-world testing environments while the city receives innovative solutions. Getting Started Checklist: Inventory existing infrastructure and data sources Map local technology partners and resources Explore university collaboration opportunities Identify potential funding mechanisms Develop data sharing frameworks Launch pilot projects with clear metrics Remember: You don’t need to start from scratch. Look first at the infrastructure, partnerships, and data you already have. Then build incrementally, measuring results and reinvesting success into future initiatives. More in the next blog post. Need more information? Check out these resources: US Department of Transportation Smart City Challenge resources Smart Cities Council Readiness Guide National League of Cities Smart Cities Playbook American Planning Association Smart Cities Initiative Ready to be part of the urban revolution? Book a demo with Varidx today and discover how our cutting-edge technologies can transform your city!
Imagine a future where urban living is seamlessly integrated with technology, making our cities more efficient, sustainable, and livable. Welcome to our exploration of innovative urban solutions observed during our recent visit to Southeast Asia. The cities of Manila Metro, Jakarta, Nusantara, and Badung are at the forefront of smart city development, implementing cutting-edge technologies and strategies to enhance urban living. This post highlights ten remarkable initiatives that not only address pressing urban challenges but also serve as valuable examples for cities around the world. Join us as we delve into these transformative ideas that are shaping the future of urban environments. 1. Jakarta’s Smart Mobility Revolution Jakarta’s smart mobility initiative is transforming the city’s notorious traffic. AI-powered traffic lights adjust in real-time to traffic flow, reducing congestion and commute times. The city has also launched a bike-sharing system and a real-time public transport tracking app, making it easier for residents to choose eco-friendly transportation options. This holistic approach is not just easing traffic; it’s also reducing the city’s carbon footprint. 2. JAKI: Jakarta’s Super App The JAKI app is Jakarta’s digital Swiss Army knife. It allows residents to report city issues, book public services, and even register marriages online. During the pandemic, it became a crucial tool for COVID-19 information and vaccination bookings. The app’s success lies in its user-friendly interface and constant updates based on citizen feedback, making it a model for other cities looking to digitize their services. 3. Badung’s Command Center: Mission Control for Cities Badung’s Command Center is the nerve center of the city’s smart operations. It integrates data from various sources, including traffic cameras, weather stations, and emergency services, to provide real-time insights and facilitate quick decision-making. The center has been particularly effective in managing natural disasters, coordinating responses to floods and landslides with unprecedented efficiency. 4. Bali ASECH: Digital Ecosystem on Steroids The ASECH (ASEAN Smart Cities and Economic Hub) in Bali is more than just an innovation center; it’s a catalyst for regional cooperation. It hosts regular hackathons and smart city challenges, bringing together minds from across Southeast Asia. The center has already incubated several successful startups focusing on urban solutions, from smart agriculture to AI-powered tourism services. 5. Manila’s Smart City Swagger Manila’s recent smart city award from the International Data Corporation (IDC) recognizes its innovative approach to urban challenges. The city has implemented a smart flood control system that uses IoT sensors to predict and manage flooding. Additionally, Manila’s shift to digital payments for government services has significantly reduced corruption and improved efficiency, setting a benchmark for other cities in the region. 6. Nusantara: The Green Dream Nusantara, Indonesia’s planned new capital, is designed with sustainability at its core. The Nusantara Capital City (IKN) will help Indonesia achieve its target of becoming a developed country by 2045, as outlined in the Indonesia 2045 Vision. Beyond the impressive 70% green space allocation, the city plans to use autonomous electric vehicles for public transport and implement a smart grid system for efficient energy distribution. Nusantara’s ambitious plans serve as a living laboratory for sustainable urban development practices. We saw these small truck size boxes converting humidity in the air to drinking water. 7. Badung’s Trash Talk Badung’s smart waste management system is revolutionizing how the city handles refuse. AI-powered sorting facilities can identify and separate different types of waste with high accuracy, significantly improving recycling rates. The system also includes smart bins that compact waste and signal when they need emptying, optimizing collection routes and reducing the carbon footprint of waste management vehicles. 8. Manila’s Data-Driven Decisions Metro Manila’s embrace of data analytics is reshaping urban governance. The city uses predictive analytics to anticipate crime hotspots, allowing for more efficient police deployment. In education, data analysis has helped identify at-risk students, enabling early intervention programs. This data-driven approach is not just improving services; it’s also increasing trust in local government by making decision-making processes more transparent. 9. Jakarta’s Safety Net Jakarta’s smart surveillance system goes beyond just cameras. It incorporates AI-powered facial recognition and behavior analysis to detect potential security threats. However, the city has also implemented strict data protection policies to address privacy concerns. The system has not only improved public safety but also aided in disaster management, helping to coordinate evacuations during flooding events. More on our Jakarta visit here. 10. Nusantara’s Inclusive Future Nusantara’s commitment to inclusivity is evident in its urban planning. The city is designing accessible public spaces and implementing universal design principles in its infrastructure. The plan calls for keeping more than 60% of the city green – trees, trails, greenways. Nusantara plans to offer free coding and digital literacy classes to ensure all residents can benefit from and contribute to the city’s smart initiatives. This approach could set a new standard for social equity in smart city development. These innovations show how Southeast Asian cities are leading the way in urban transformations. They’re not just implementing cool tech; they’re addressing real urban challenges and improving quality of life for their residents. These examples are great use cases for cities around the world adapting and implementing similar solutions to create smarter, more livable urban environments. A recent Ipsos Predictions Survey 2025 – shows level of optimism in each country. How much do you think Smart City conveniences contribute to the high levels of optimism in Philippines and Indonesia? Got any thoughts on these innovations? Drop a comment below! And hey, maybe your city will be the next smart city superstar! Ready to be part of the urban revolution? Book a demo with Varidx today and discover how our cutting-edge technologies can transform your city!
Explore Manila’s Smart City Revolution: Innovations for a Sustainable Future Welcome to the Varidx Blog! Join us on an exciting journey through the bustling metropolis of Manila, where innovation meets tradition in the heart of the Philippines. Smart City Initiatives: Paving the Way for a Brighter Future Pioneering Projects Our visit to Manila was part of the U.S. Trade Mission focused on Innovative Technologies for Urban Infrastructure Development. This event brought together American companies and local leaders from various cities, including Makati. During the mission, mayors from different parts of Manila shared their projects and ideas. It was inspiring to hear about their efforts to make their cities smarter and more livable. The discussions highlighted how important it is for cities around the world to work together and learn from each other. The trade mission was a great opportunity to explore how U.S. technologies could help support Manila’s goals for urban development. It reminded us that collaboration is key when it comes to tackling challenges in our cities. As we stepped off the plane into the warm, tropical air of Manila, we could feel the energy of a city poised for change. Our recent visit as part of the U.S. Trade Mission for Innovative Technologies for Urban Infrastructure Development opened our eyes to the incredible potential of this vibrant capital. Metro Manila is leading the charge in the Philippines’ Digital Transformation. Cities in the National Capital Region and outside, including —Makati, Muntinlupa, Caloocan, Pasig, and Quezon City , Cebu, Davao, and Clark—are trailblazing the path towards a smarter, more connected urban landscape. These cities are part of an ambitious plan to transform 80 Philippine cities into smart and sustainable communities by 2028. Technology at the Heart of Change Walking through the streets of Manila, we witnessed firsthand how technology is reshaping urban life. From smart traffic management systems to innovative waste disposal solutions, the city is embracing cutting-edge technologies to enhance various aspects of urban living. According to the Makati City Mayor Mar-Len Abigail Binay, the city uses data analytics to track Air Quality, Water and population health. CCTV Cameras are used for surveillance. Deploying several hundred Disaster Risk Reduction Management (DRRM) vehicles earned Makati a nomination to finalist for World Smart Cities Awards. Technology is in the city Mission: “The Makati City Government will be the model for world-class local governance: providing for the well-being of its citizenry through delivery of the highest level of basic, social, and economic services with breakthrough technologies, sustainable financing, and competent, responsible and professional civil servants” Collaboration: The Key to Success What struck us most was the spirit of collaboration driving Manila’s smart city initiatives. Government agencies, local authorities, and international partners are working hand in hand to bring this vision to life. The U.S. Trade Mission’s involvement underscores the global interest in Manila’s transformation. Sustainability: More Than Just a Buzzword Manila’s commitment to sustainability is evident in every corner of the city. From green spaces sprouting amidst concrete jungles to eco-friendly public transportation options, the city is taking concrete steps towards a greener future. Davo – Plastic Smart City The Plastic Smart Cities initiative in Davao City, implemented by WWF, focuses on reducing plastic pollution through innovative waste management solutions. Davao City, known for its rich cultural heritage and the annual Kadayawan festival, faces challenges in waste collection, especially in remote barangays. The initiative targets three types of barangays: high-end, Ru-Ban (rural-urban), and low-income. Key interventions include providing plastic shredders, supporting women’s organizations in waste segregation and upcycling, and establishing community gardens. Notable projects include the Toril Kamlabuan Association’s upcycling efforts and the Women’s Bright refilling station. These efforts aim to enhance waste management, promote sustainability, and reduce plastic pollution in Davao’s diverse communities. A City That Cares Perhaps the most heartening aspect of Manila’s smart city initiatives is the focus on improving the lives of its residents. Enhanced public services, powered by data analytics and smart technologies, are making government more responsive and efficient. The Road Ahead As we bid farewell to Manila, we left with a sense of excitement for what the future holds. The city’s smart initiatives are not just about technology—they’re about creating a more livable, sustainable, and prosperous urban environment for all. Experience the Future with Varidx Are you inspired by Manila’s journey towards becoming a smart city? At Varidx, we’re at the forefront of urban innovation, developing solutions that can help cities like Manila realize their smart city dreams. Ready to be part of the urban revolution? Book a demo with Varidx today and discover how our cutting-edge technologies can transform your city!


![Bus Stop [Frepik https://www.freepik.com/]](https://varidx.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/82645369_9844304-scaled.jpg)